Consulting services Hydrology and hydraulic engineering
Hydrologic modelling with HEC-HMS e hydraulic simulations with HEC-RAS
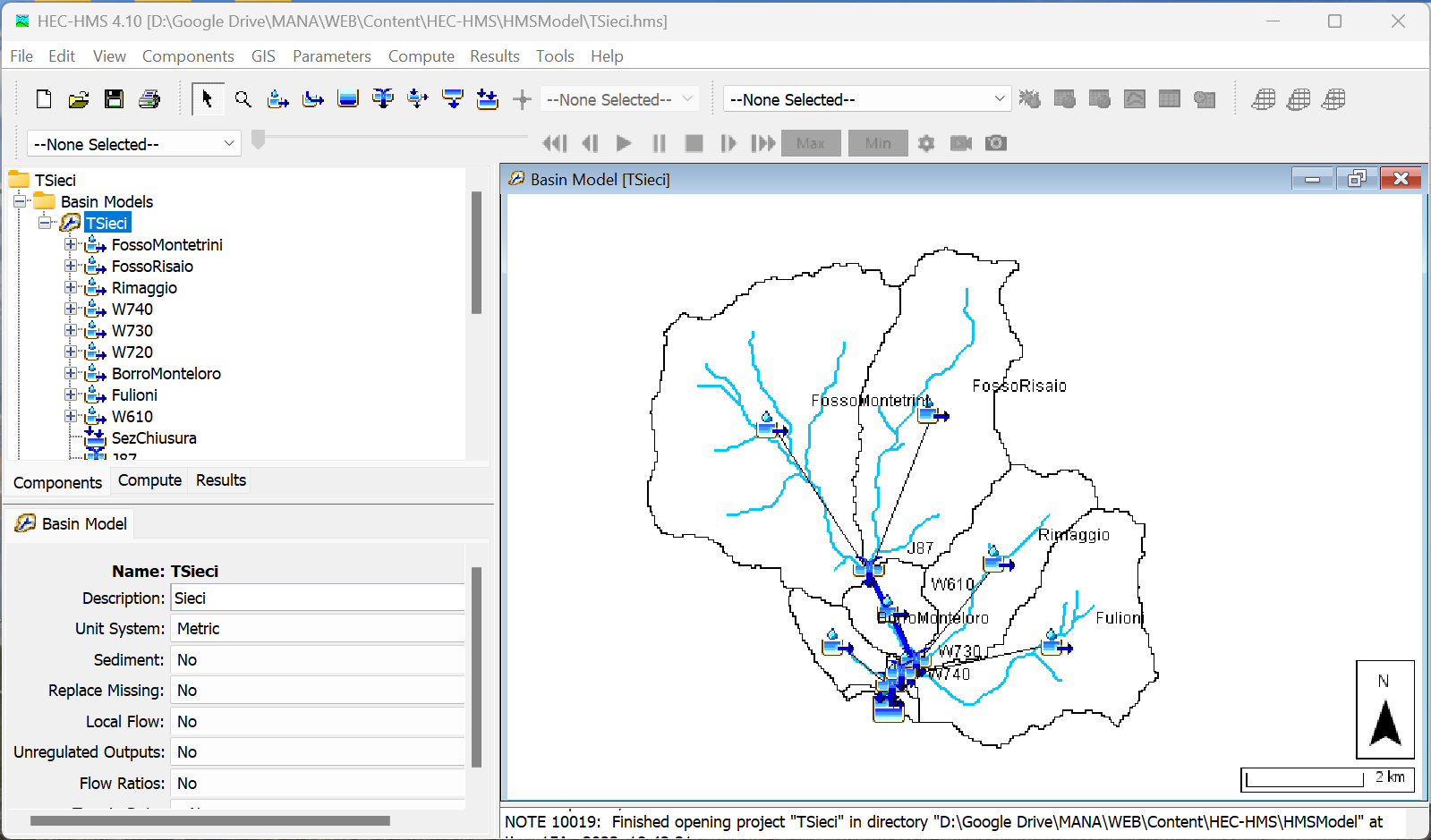
Hydrologic modelling: HEC-HMS
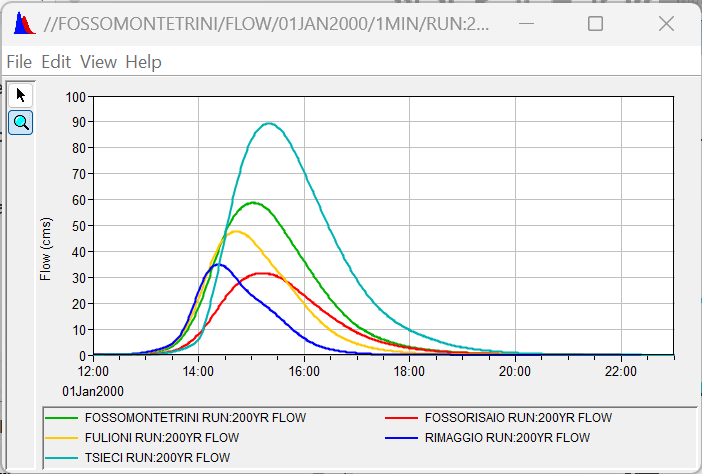
The Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) is a software for the simulation of hydrologic processes in watershed systems affected by meteorological events of known characteristics.
The software is frequently applied to modeling flood events, particularly to calculate design hydrographs for use in hydraulic simulations with other software (e.g., HEC-RAS).
Moreover, it can also be applied in water balance modeling, for estimating the water resource available for withdrawals (irrigation, industrial use, for drinking purposes, hydropower) and their impacts on water bodies.
Links:
US Army Corps of Engineers | Hydrologic Engineering Center
Hydraulic simulations: HEC-RAS
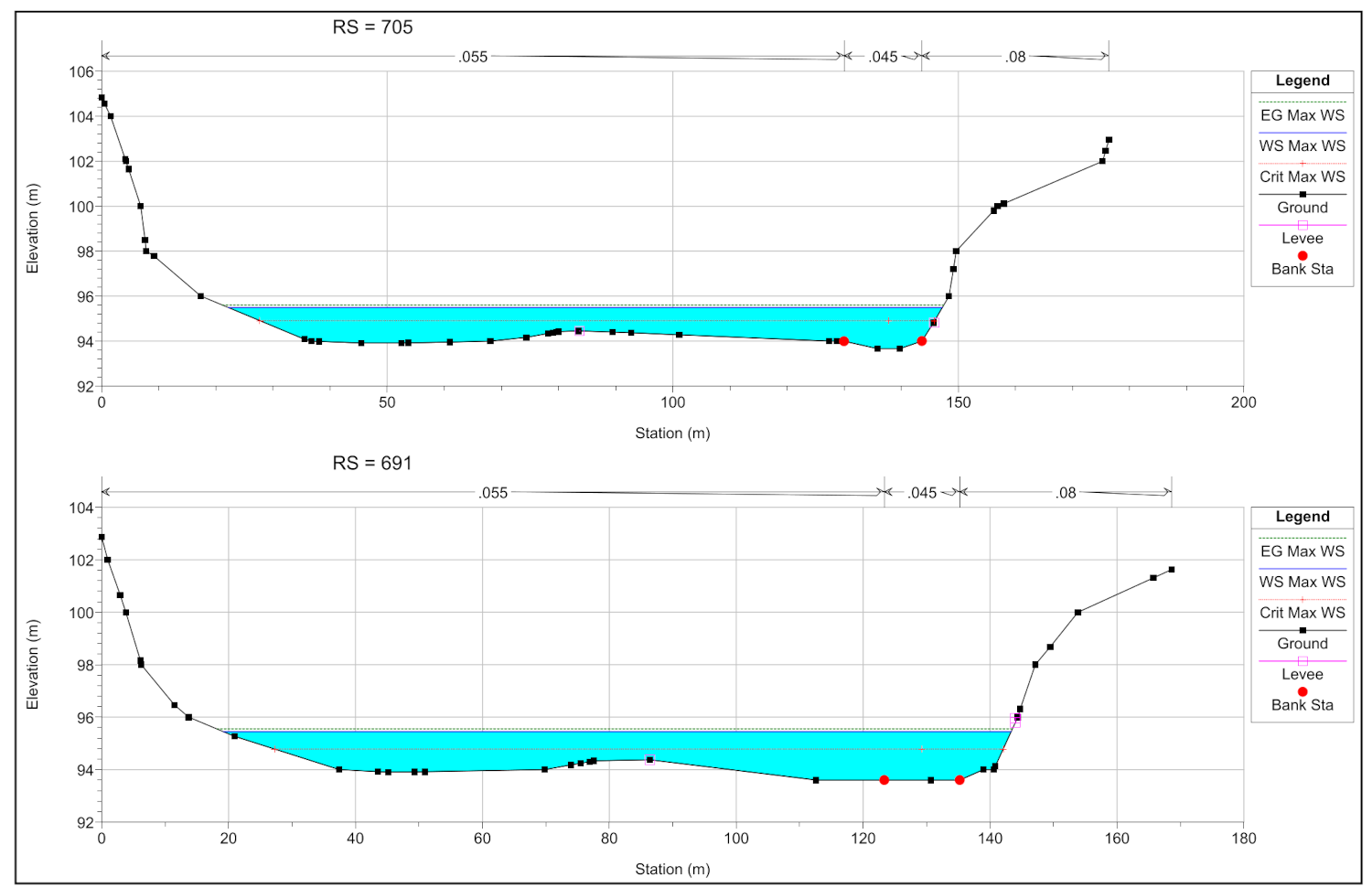
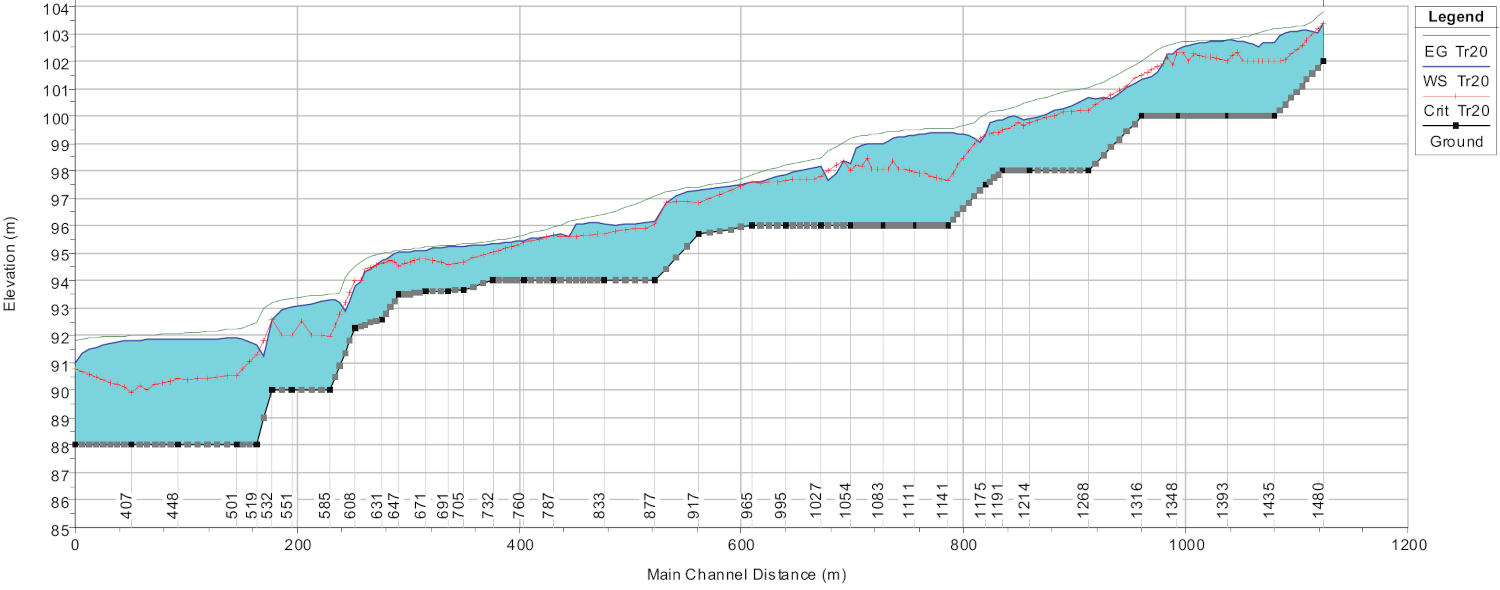
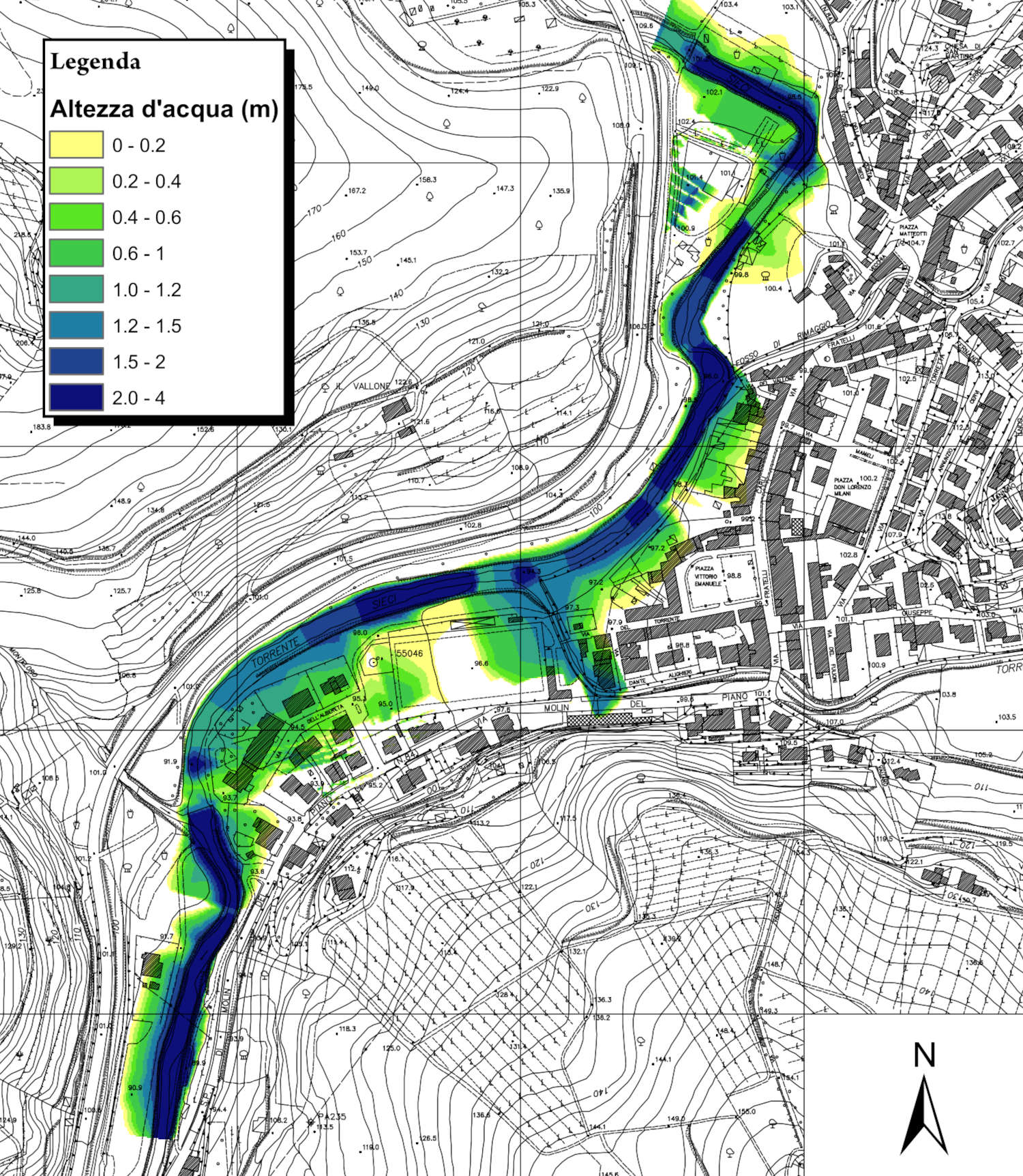
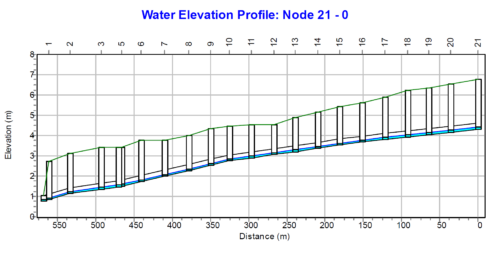
HEC-RAS (Hydrologic Engineering Centers River Analysis System) is a widely used software package developed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers for hydraulic analysis of river systems. It is designed to simulate the flow of water in rivers or artificial channels and provides engineers with a comprehensive set of tools for analyzing and predicting water flow behavior and modeling of complex hydraulic phenomena, such as flood propagation, solid transport, and flooding.
The HEC-RAS system contains the following river analysis components for different flow regimes, including one-dimensional (1D) steady flow water surface and one-dimensional and/or two-dimensional (2D) unsteady flow simulation. In addition, particularly for flood simulation, 1D simulations of the river bed can be coupled with 2D models of flood areas.
HEC-RAS is widely used to carry out hydraulic assessment, as support for the design of hydraulic works and the planning and verification of structural interventions for hydraulic risk mitigation.
Typical uses include:
- simulation of hydraulic profiles and reconstruction of water heights;
- delineation of flood-prone areas;
- sediment transport modelling and prediction of geomorphological evolution of the riverbed;
- bridge scour computations;
- the evaluation of flood protection methods (e.g., detention basins);
- contaminant transport and water quality;
Links:
US Army Corps of Engineers | Hydrologic Engineering Center
Water networks
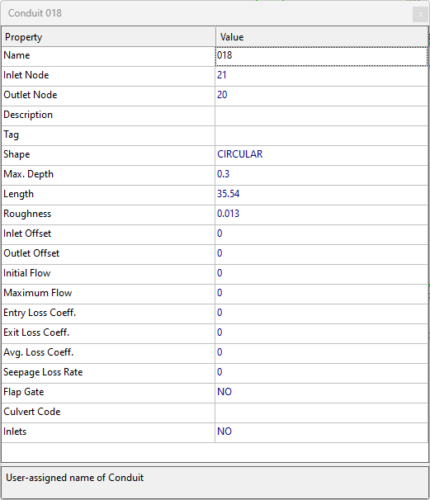
Modeling, design, and verification of sewer systems with SWMM
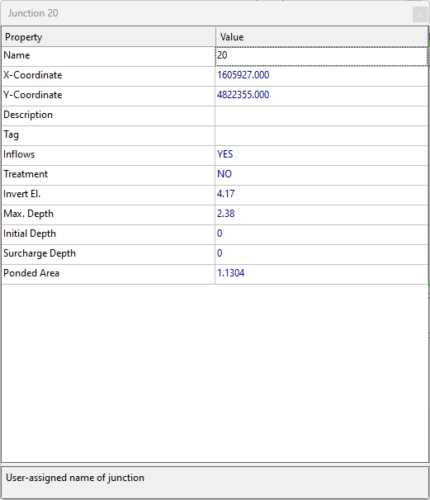
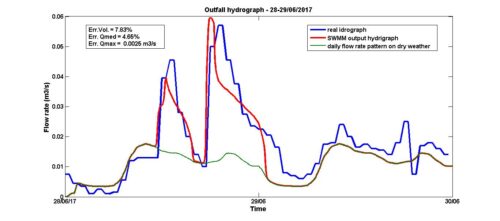
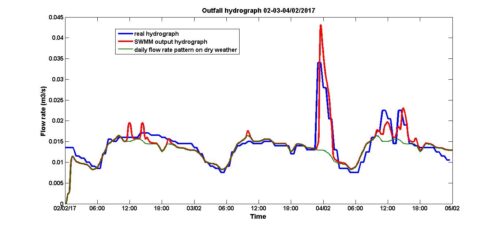
SWMM
Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) is a software that is widely used to simulate stormwater runoff in urban catchments through channel and pipe networks. It is utilized for a variety of purposes including the analysis and design of combined sewers, sanitary sewers, implementation of real-time control strategies, and the design of drainage system components such as flood control systems, storage tanks, pumping stations, and low impact development systems (LIDs).
SWMM consists of three main software components:
- Runoff (hydrologic) module, which simulates the hydrologic processes that produce runoff from urban areas.
- Routing (hydraulic) module, which routes runoff and external inflows through the drainage system network of pipes, channels, storage/treatment units and diversion structures.
- Water quality module, which estimates the production of pollutant loads associated with stormwater runoff and routes water quality constituents through the drainage system.
SWMM has a range of typical applications, including:
- Planning, design and sizing of drainage systems
- Simulation of network behaviour for single rainfall events or long-term periods
- Design of flow dividers, pumps, weirs, storage/treatment units
- Design of low impact development (LID) such as green roofs, infiltration trenches, permeable pavement systems, rain gardens.
- Simulation of the generation, inflow and transport of pollutants in the network for the evaluation of mitigation actions.
Links:
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA)
pySWMM: advanced modelling
With MatSWMM and pySWMM toolboxes, we are able to integrate the SWMM simulation engine into other custom or previously developed software or applications. Here are some examples:
- Integration with existing monitoring systems (remote control, SCADA). Real-time control logics for the management of hydraulic systems can be defined to minimize operating and maintenance costs.
- Optimization of pumping systems (e.g., reducing energy consumption in pumping systems).
- Targeted actions at critical points in the network for flood prevention.
Design and verification of water distribution networks with EPANET
EPANET
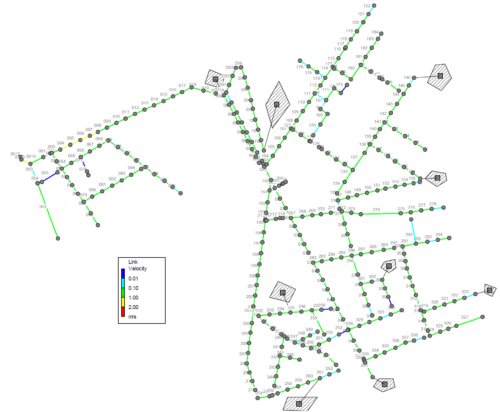
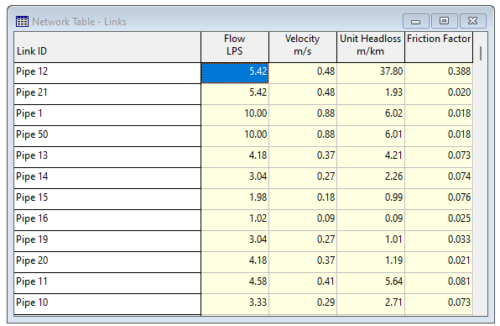
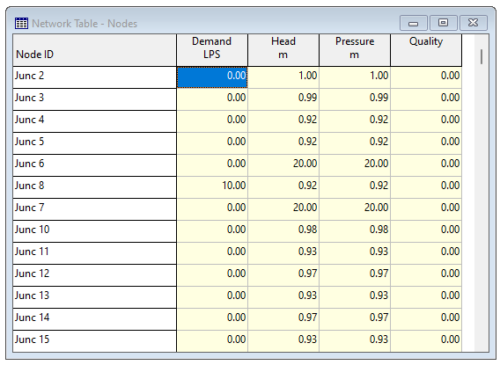
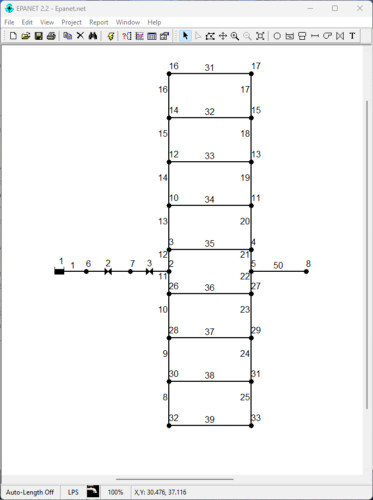
EPANET is a software application developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) used for the design and verification of water distribution systems. In EPANET the distribution networks, which can also present a complex topology, are represented as a set of links and nodes. The software simulates both the water flow and water quality in each node and link of the network. The typical outputs from the calculations are: the flow rates in nodes and links, the fluid velocity, the pressure in each node, the concentration of dissolved chemical constituents, and reservoir levels.
The most common EPANET applications include:
- design and sizing of new water distribution networks (e.g., drinking water, industrial or fire-protection supply)
- retrofitting of existing infrastructure
- estimation of water levels inside tanks and optimization of energy consumption for pumping
- transport of contaminants or disinfectants (e.g., chlorine) in the network
Links:
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA)